Dirac notation or bra-ket notation is a way of writing quantum
- bra = linear function of a vector
- ket = vector
and are orthogonal and are normalized and are orthonormal (both orthogonal and normalized)
Kronecker delta shows orthonormality where
- when n m ,
- when n m,
Projection = the coefficient is the projection of onto the vector
Dirac delta function = or
closure relation An orthonormal basis set is a basis set if for every function , the function can be expressed in
sifting property of the Dirac delta function
Inner product in Position representation =
Hilbert space
Hilbert space is similar to a vector space
- Hilbert space is linear
- inner product exists
- length of vector =
The state of a quantum system is characterized by its state vector which is an element of the Hilbert space. All physical information about the given system is in its state vector
To say that a quantum system characterized by an n-dimensional Hilbert state means that each possible state of the system can be represented by a state vector with n complex components, and can be written as
The n-dimensional Hilbert space will have n basis, so that the state vector can be represented as:
While the state vector itself is basis-independent, the values of its components will depend on the choice of basis.
example An electron spin (up and down) system is a two-dimensional Hilbert space with the two basis being “up” and “down”, so that a general element in the Hilbert space can be represented as
basis sets
Discrete orthonormal basis set orthogonal =
spans the space =
Continuous orthonormal basis set orthogonal =
spans the space =
generalization of continuous basis set the wave function can be expressed as
where
In dirac notation =
where
Operators
state vectors are modified by linear operators that act upon them and that determine their physical properties
observables = a mathematical transformation between two elements of a given Hilbert space and are represented by operators
The expectation value associated to a measurement of the physical observable given a quantum state is:
Given that the outcome of any measurement is a real quantity, the expectation value is real for any operator in any given quantum state. In other words, operators representing physical observables must satisfy
these operators are called Hermitian operators which are by definition equal to their conjugate
- Hermitian operators have associated real eigenvalues
- The eigenvectors and associated to different eigenvalues () are orthogonal
- The eigenvectors of a Hermitian operator span the complete Hilbert space and so represent a complete basis in the Hilbert space
The Heisenberg uncertainty principle is the consequence of the axiom that all physical observables in quantum physics are represented by Hermitian operators
Eigenvalue equations
Eigenvalue equations = where
- represents a square matrix of dimensions
- is a column bector with dimensions n
- is the eigenvalue of the equation and is the eigenvector
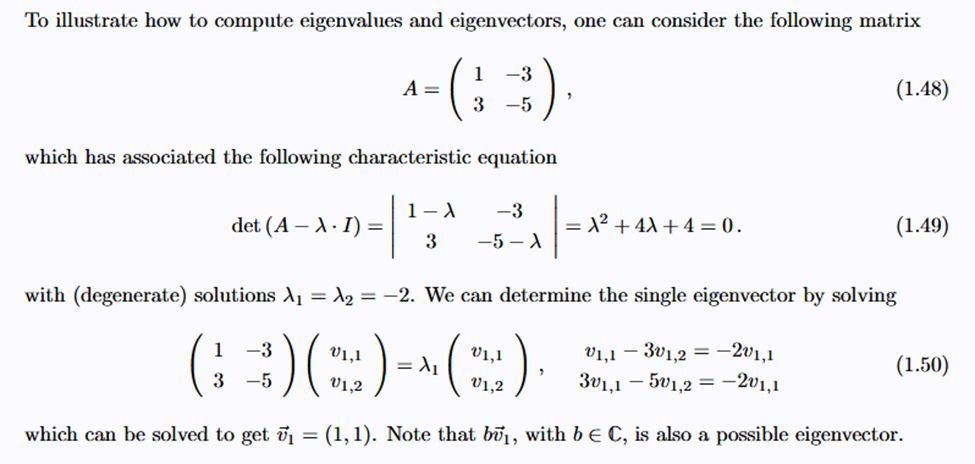
To find the eigenvalues =
- Find the characteristic equation of the matrix A
Where is the identity matrix and det is the determinant. This gives the eigenvalues 2. Find the eigenvectors by solving
Position representation
Position space is the set of all position vectors r in Euclidean space, and has the dimensions of length, where a position vector defines a point in space.
The wave function is represented as
Position operator ()
The position operator has the position of a quantum mechanical particles as eigenvalues
expectation value of the position components of a particle =
momentum representation
wave function in momentum representation =
inner product in momentum representation =
momentum operator
- in the momentum representation =
- in position representation =
expectation value